Learning Experience Platforms or Learning Analytics: Value-Add or Challenge
In a world where continuous learning determines business success, modern organizations are faced with the challenge of choosing the right technology to support employee development. Learning Experience Platforms (LXP) and Learning Analytics are two advanced approaches that build on existing Learning Management Systems (LMS) while offering new potential for personalizing and optimizing learning processes.
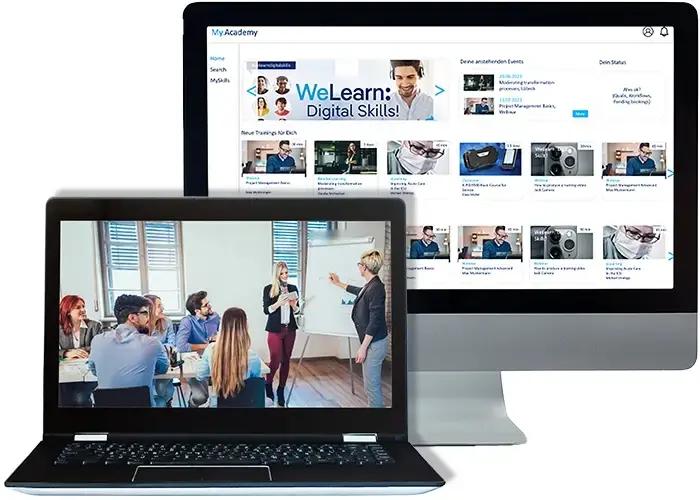
But which solution is the right fit? This page explores the differences, benefits, and challenges of both approaches and provides practical tools to help you make an informed choice.
By the end of this text, you will have a clear understanding of which solution—LXP or Learning Analytics—better suits your organization’s needs. Through critical analysis and a useful checklist, we will equip you with the tools to make a well-informed decision and enhance your learning strategy effectively.
1. The Future of Learning in Companies
Modern companies face the challenge of continuously upskilling their employees to remain competitive. In this context, Learning Management Systems (LMS) have played a central role for years, allowing for structured management of training and development programs.
With the emergence of Learning Experience Platforms (LXP) and data-driven approaches like Learning Analytics, new opportunities arise to further personalize and optimize learning processes. But do LXPs now replace Learning Analytics or LMS, or do they merely complement them? These questions will be critically discussed below to help companies make informed decisions.
2. Learning Experience Platforms (LXP): A New Learning Landscape
Learning Experience Platforms (LXP) are designed to make learning more individualized and experience-oriented. While they are based on existing LMS, LXPs expand them with innovative features that focus more on the learning behavior of users. LXPs emphasize a high degree of personalization, offering dynamic learning suggestions based on learners' preferences and behavior.
- Definition and Functionality of LXP:
LXPs provide a user interface tailored to the individual learner. Unlike LMS, which focus on managing and delivering learning content, LXPs optimize the user experience by offering personalized learning recommendations. This means that learning paths are not pre-defined but are dynamically adjusted based on the learners' needs.
- Advantages of LXP Compared to LMS:
While modern LMS can manage various learning formats—from online courses to in-person seminars and blended learning concepts—the key advantage of LXPs lies in the automated, AI-driven personalization. They continuously analyze learner behavior and progress, recommending tailored learning content accordingly. This can boost motivation, as learners are presented with content that is immediately relevant to them.
- Challenges in Implementing LXP:
Implementing an LXP requires close integration with existing LMS systems and a well-defined data strategy. Companies must ensure that data from the LMS is processed correctly to enable personalization through the LXP. Additionally, using AI and big data technologies can place high technological demands on the infrastructure.
3. Learning Analytics: Data-Driven Learning in Focus
Learning Analytics allows companies to gain insights into their employees' learning habits and measure the success of learning programs. By analyzing learning data, targeted improvements can be made to optimize both the learning experience and outcomes.

- Definition and Functionality of Learning Analytics:
Learning Analytics refers to the systematic collection and analysis of learning data. This data can provide insights into which learning content is most effective, how long learners take to complete tasks, and where learning barriers might arise.
- Advantages of Learning Analytics:
Learning Analytics offers data-driven decision-making. For example, it can reveal which courses have the highest completion rates or where learners tend to drop out. This allows for targeted adjustments to learning content. A Deloitte study shows that companies using Learning Analytics can improve their training success by up to 25%, thanks to data-informed decisions.
- Limitations of Learning Analytics:
Despite its advantages, there are challenges in using Learning Analytics. A major issue is that data may not be meaningful if the underlying data quality is poor. Additionally, interpreting the data can be problematic, as correlations can easily be misunderstood. For instance, a high completion rate might indicate overly simplistic content rather than program success.
4. LXP vs. Learning Analytics: Who Takes the Lead?
LXP and Learning Analytics pursue different approaches, but both aim to make corporate learning more effective. While LXPs tailor learning more closely to the individual user, Learning Analytics provides the data needed to improve the overall system. The question is whether one system can replace the other or if a combination is more effective.

- Personalization:
LXPs provide strong personalization by analyzing user behavior and continuously recommending content that benefits the learner the most. Learning Analytics, on the other hand, works on an aggregate level, analyzing learning behavior across all users to drive general improvements. The two systems complement each other in this regard, as they offer different levels of analysis and personalization.
- Data Quality and Volume:
Both LXPs and Learning Analytics rely on analyzing large datasets. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring data quality. For meaningful Learning Analytics, the data must be consistent, complete, and accurate. LXPs, on the other hand, need relevant and up-to-date data to make useful recommendations based on AI algorithms.
- Integration with Corporate Culture:
The success of either system depends heavily on the company’s culture. In a data-driven environment, Learning Analytics can be highly effective. In companies that prioritize the individual development of their employees, LXPs with their personalized approach can be better integrated.
5. Technical Requirements and Challenges in Implementation
The successful implementation of a Learning Experience Platform (LXP) or Learning Analytics depends on a well-thought-out technical infrastructure. Key factors include the integration of existing systems, data security, and handling large data volumes.
Data Integration and IT Infrastructure
One of the biggest challenges in adopting LXPs and Learning Analytics is seamless integration with existing Learning Management Systems (LMS). LMS typically serve as the central platform for managing learning content, courses, and participant data. For LXPs or Learning Analytics to reach their full potential, they must access the same data and communicate with the LMS in real time.
- Requirements for Data Integration:
To ensure optimal integration, companies need to confirm that their LMS can export, analyze, and re-integrate data. Systems that support open standards like xAPI (Experience API) or SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) are better suited for integration, as they provide unified data formats and easy communication between systems. Companies should also consider cloud-based technology, which offers greater scalability and flexibility.
- Data Volume and Processing Capacities:
Both Learning Analytics and LXPs generate and process vast amounts of data, especially when AI algorithms are used for personalization. Therefore, sufficient storage and processing capacities are required. A Gartner report indicates that many companies underestimate the computational and storage demands of their existing systems, leading to performance issues.

Data Protection and Security
Data security and privacy are crucial, as LXPs and Learning Analytics collect large amounts of personal data, including learning behavior, progress, and outcomes. Compliance with privacy regulations like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is mandatory to avoid legal problems.
- Ensuring Data Security:
Strict security protocols, such as data encryption, secure user access, and regular security audits, should be implemented. A multi-tiered permission system can ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data.
Training and Change Management
Beyond technical infrastructure, it is essential to train staff in the use of new systems. A robust change management program should ensure that employees understand the benefits of the new technologies and actively participate in the implementation process.
6. Are the Measurements Meaningful? A Critical Reflection
Learning Analytics and the measurements generated by LXPs offer many advantages, but only if the data is accurately captured and interpreted. In practice, there are often significant differences in data quality that can greatly affect the significance of analyses.
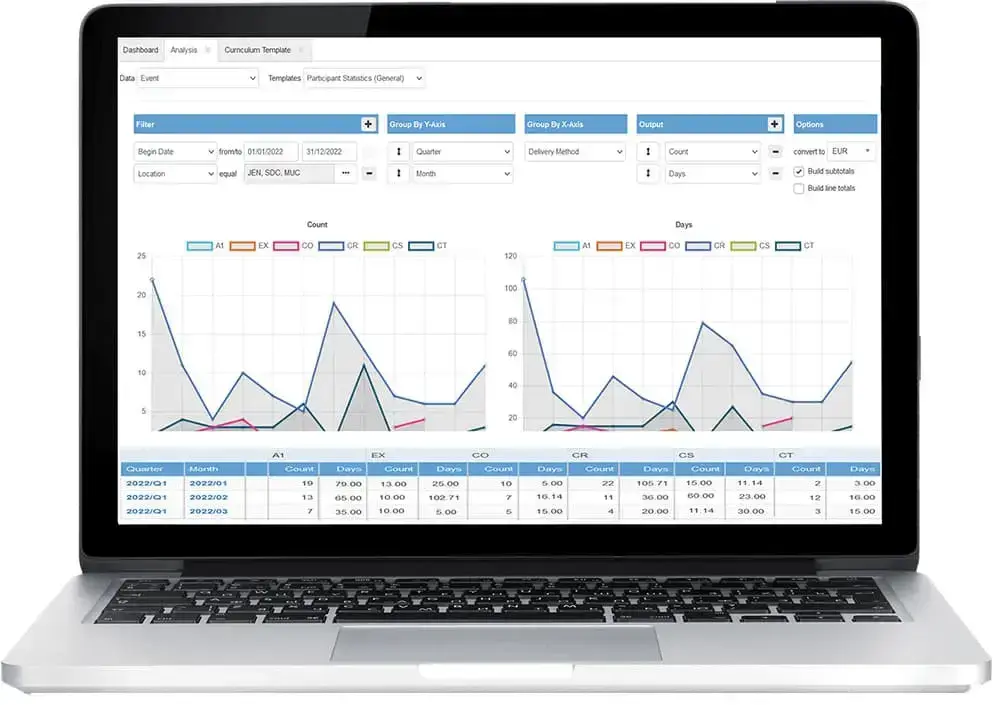
Issues with Data Interpretation
Simply collecting data does not automatically lead to better learning processes. Data is often misinterpreted or misunderstood, leading to erroneous conclusions. A common mistake is viewing data in isolation without considering the overall learning environment. For example, a high completion rate in an online course might be seen as a positive sign, even though the course content may not be sufficiently challenging.
- Correlation vs. Causality:
It is important to distinguish between correlation and causality. High engagement in a course may correlate with high learning success, but the reasons could be varied—such as high learner motivation or external incentives that are unrelated to course content.
Poor Data Quality
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring data quality. Incomplete or incorrect data inevitably leads to inaccurate analyses. According to an IBM study, up to 30% of the data collected in many companies is lost or unusable due to poor quality.
- Examples of Poor Data Quality:
If learning times are not properly recorded or participant profiles are not regularly updated, personalization features in LXPs may provide incorrect recommendations. This results in learners receiving content that does not match their current needs.
What Numbers Don’t Show: Qualitative Aspects of Learning
Numbers alone often don’t tell the whole story. Even if data shows which courses or learning methods are effective, they reveal little about actual learning processes and experiences. For example, a course may have high completion rates and good test results, but still fail to equip learners with the necessary competencies if the knowledge gained is not sustainable.
7. Pragmatic Alternatives and Recommendations for Improving Learning Efficiency
Not every company has the resources or technological maturity to fully implement an LXP or comprehensive Learning Analytics. However, there are still approaches that can enhance learning efficiency, even with limited means.

Gradual Adoption of Learning Analytics
Instead of implementing a full-scale solution right away, companies can take initial steps by using Learning Analytics on a basic level. One example is utilizing the reporting and dashboard features of an existing LMS to conduct initial analyses of learning progress and completion rates.
- Pilot Projects for Implementation:
Companies can launch small pilot projects to gain experience with Learning Analytics. This allows them to evaluate how deeper analytics can be applied based on the results.

Combining LXP and LMS
Many companies can maximize the value of an LXP by integrating it as an extension of an already established LMS. This allows personalized learning suggestions and dynamic learning paths to be introduced, while the LMS continues to manage courses, certifications, and formal learning formats.
- Leveraging Blended Learning Concepts:
By combining formal courses of various learning formats (LMS) with personalized learning paths (LXP), companies can create a more comprehensive and flexible learning offering that supports both structured and informal learning methods.

Utilizing Feedback and Qualitative Data
Even without large-scale technical solutions, incorporating qualitative feedback can be a valuable addition. Regular surveys or direct learner feedback provide insights into how content is perceived and where improvements are needed.
- Incorporating Qualitative Data:
Rather than relying solely on numbers, companies can also integrate employee feedback into the decision-making process. This can be especially valuable in determining whether the learning content is being applied in the workplace.
8. Checklist: Prerequisites for Implementing LXP and Learning Analytics
Before a company invests in a Learning Experience Platform or Learning Analytics, it should assess its own infrastructure and resources, to identify whether the technical and organizational prerequisites are sufficient.
With the following checklist, training academies and HR departments can make informed decisions about whether implementing an LXP or Learning Analytics is practical and feasible. Ultimately, the success of these technologies depends on the technical infrastructure, data quality, and readiness for change.

Technical Infrastructure
- Does the company have a modern LMS that supports xAPI or SCORM?
- Are sufficient storage and processing capacities available to handle large data volumes?
- Is there a cloud infrastructure that offers flexibility and scalability?
- Are the necessary interfaces available to integrate data from various sources?
Data Quality
- Is learning data regularly collected and complete?
- Are there mechanisms in place to review and ensure data quality?
- Are regular data backups and security measures in place?
Data Privacy and Security
- Are all systems GDPR-compliant and aligned with applicable data privacy laws?
- Are there clear security protocols in place to protect personal data?
- Are employees and learners informed about how their data is handled?
Organizational Prerequisites
- Is there a willingness to implement new learning technologies and accept changes in the learning process?
- Does the company have sufficient internal resources or external support to maintain and optimize the systems?
- Are training programs for employees and learners planned to facilitate the transition to a new platform?
Practical Implementation and Pilot Projects
- Is it possible to launch small pilot projects to test the systems on a limited scale?
- Is there a willingness to make adjustments based on pilot project outcomes and iteratively improve learning systems?
9. Decision Support: LXP or Learning Analytics – Which Fits Your Requirements Better?
Before choosing a Learning Experience Platform (LXP) or Learning Analytics, it’s essential to carefully assess your organization’s specific needs, to identify the best solution for your company.
The following checklist provides practical guidance for understanding your organization’s specific requirements and selecting the right solution. Whether you opt for an LXP or Learning Analytics, it’s crucial that the chosen technology supports your learning objectives and contributes to enhancing the learning experience.

Resources for Implementation
Do you have the internal resources and expertise for implementation?
- Yes: Both options are feasible.
- No: A LXP may be easier to implement, as it often offers more user-friendly interfaces.
Goals and Priorities
Do you want to personalize the learning experience?
- Yes: An LXP might be the better choice.
- No: Learning Analytics may suffice.
Type of Learning Content
Do you primarily offer formal training?
- Yes: An LMS with Learning Analytics might be sufficient.
- No: An LXP could be beneficial to support informal learning.
Data Integration
Does your organization have the necessary systems for data integration?
- Yes: Both systems could be considered.
- No: You may need to invest in your technical infrastructure first.
Budget and Costs
What financial resources are available to you?
- Limited: Learning Analytics could be more cost-effective.
- Flexible: Investments in an LXP might pay off in the long run.
Culture and Acceptance
Is your leadership ready to embrace new learning technologies?
- Yes: Both systems can be successfully implemented.
- No: Start with a solution that may encounter less resistance.
Feedback Mechanisms
Do you already have established mechanisms for collecting user feedback?
- Yes: Use this data to support both an LXP and Learning Analytics.
- No: Start with an LXP to integrate real-time feedback.
Ready for the Future?
The educational landscape is changing rapidly—be prepared to implement innovative solutions and seize the opportunities that arise. Utilize the possibilities offered by modern seminar management software and LMS to optimize your offerings and meet the needs of your participants.

About Us
Since 1998 SoftDeCC is working closely with major training centers and academies. This results in a unique experience with training requirements.
Our Learning Management System TCmanager® is designed to adjust to individual corporate learning processes and address evolving challenges. More...

Free Consultancy
Discuss your Training Challenge with us.
Call +49 (0)89 / 309083930 to arrange for your free consultancy.
.webp)





