LMS Features for empowering Corporate Learning as a Service
Is CLaaS a Business Model for you?
In today's digital and fast-paced business environment, companies must continually educate their employees to remain competitive. Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) offers an innovative solution that extends beyond traditional internal training. This model allows companies to commercialize their internal learning resources by offering them as a service to external organizations.
The concept is supported by a powerful Learning Management System (LMS), which manages internal training efficiently and enables the external sale of learning programs.
1. Introduction to the Business Model
The CLaaS business model is designed to sell training programs and content as a service to external companies. This model allows companies to monetize their training resources while providing users with access to high-quality content without needing their own infrastructure.
Companies offer modular learning content that can be adapted to the needs of various industries. A key element of this model is the scalability of the offerings, made possible by a powerful LMS.
Core Offerings and Services:
- Modular Training Programs: Companies can offer industry-specific training modules. For example, an IT security course could be tailored specifically for the financial sector to meet current regulatory requirements.
- Blended Learning: Combination of online training with in-person sessions, such as practical workshops.
- Certifications: Automated certification processes that help companies regularly qualify their employees and document the necessary proof.
Pricing and Revenue Models:
- Subscription Models: Companies pay for continuous access to training content, similar to software-as-a-service.
- Pay-per-Use: Flexible pricing model suitable for companies with specific training needs.
- White-Label Solutions: Companies can use the platform with their own branding, allowing them to market training services under their own name.
Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) vs. Training as a Service (TaaS)?
Both terms—Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) and Training as a Service (TaaS)—describe similar business models where training offerings are provided as a service.
However, there are differences and nuances that influence how these terms are used in different contexts.
- Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS): This term is commonly used when the training offerings are specifically tailored to the needs of companies (Corporate Learning).
LaaS encompasses comprehensive learning programs that can be offered both for internal employee development and to external customers of a company. It focuses on integrating learning into corporate workflows and managing complex training structures.
CLaaS is often offered by companies that already have in-house training resources and want to monetize them.
- Training as a Service (TaaS): TaaS is a broader term, used to describe a wide range of training services delivered through cloud technologies or as on-demand services. This expression is less focused on the context of a specific company and can also refer to training offerings aimed at individuals or companies in general.
TaaS can be used by specialized training providers offering various types of courses without necessarily focusing on corporate learning.
2. Benefits of CLaaS for Training Providers and Their Clients
Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) offers numerous advantages for both training providers and their clients, enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of training programs

Benefits for Training Providers:
-
Monetization of Training Resources: CLaaS allows training providers to monetize their existing training resources and expertise. By offering their programs as a service, they can unlock new revenue streams beyond traditional training methods.
-
Scalability and Reach: With a well-implemented LMS, training providers can quickly and efficiently scale their offerings. The system enables the simultaneous delivery of training to a large number of clients without the need for additional infrastructure.
-
Flexibility in Offering Design: CLaaS provides training providers with the ability to develop customized learning solutions tailored to the specific needs of their clients. They can easily adjust and expand their programs to integrate various learning methods and styles.
Benefits for Clients:
-
Accessibility and Flexibility: Clients benefit from the flexibility to access training content anytime and from anywhere. The integration of blended learning and self-paced learning paths allows learners to adapt the training to their individual needs and schedules.
-
Cost Efficiency: By utilizing CLaaS, companies can save significant costs as they do not need to build or maintain their own training infrastructure. Instead, they pay only for the training services they actually use, leading to better cost control.
-
Access to Expert Knowledge and High-Quality Content: Clients gain access to high-quality training content and expertise that may not be available internally. CLaaS providers ensure that training materials are up-to-date and relevant, leading to continuous employee development and improvement.

3. Market Analysis and Target Groups
The global e-learning market is experiencing rapid growth. According to a report by Global Market Insights*, the market is expected to reach over $374 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by increasing digitalization and the rising demand for flexible learning solutions

- Regulated Industries: Companies in heavily regulated sectors such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and finance must regularly train their employees to meet compliance requirements. For instance, banks require continuous training on topics like anti-money laundering and data protection.
- Technology Sector: Companies like Microsoft and Google already offer CLaaS solutions to help users optimize their technology products. Microsoft's "Enterprise Skills Initiative" is an example of a successful CLaaS implementation.
- Manufacturing and Industry: The automotive industry, for example, has training needs related to new manufacturing technologies, particularly in electric mobility. Companies like Bosch use external training solutions to keep their employees updated on new production processes.
4. Essential Features of a Learning Management System (LMS) for CLaaS
The effectiveness and success of Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) rely heavily on the capabilities of a robust and scalable Learning Management System (LMS). To support both internal training programs and external distribution of learning content, the LMS must meet several key specifications.
These features ensure seamless delivery, administration, and management of various learning initiatives while maintaining flexibility and scalability.
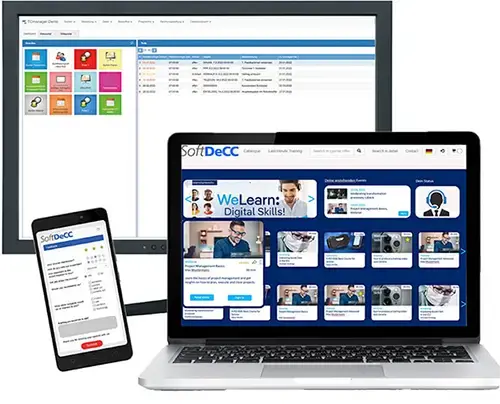
Key LMS Features for CLaaS / TaaS
Scalable Cloud Infrastructure: The LMS should be cloud-based and flexible to scale, accommodating businesses of all sizes. For example, it should handle the training needs of both multinational corporations and small businesses efficiently.
White-Label Solution: A white-label capable platform allows companies to present the training platform with their own branding, creating a cohesive user experience that aligns with their corporate identity.
Multi-Tenant Architecture: Multi-tenancy is crucial for CLaaS, where different clients (tenants) use the same LMS platform. Each tenant should have isolated data and a customized environment, allowing secure and independent management of their training programs.
Integration Capability: The LMS must integrate seamlessly with existing CRM and finance systems to streamline processes such as billing, support, and customer management.
Qualification Management
For industries with strict regulatory requirements, qualification management is an essential feature of an LMS. This function ensures that employees and external trainees complete the necessary certifications and qualifications in a structured and auditable manner. Here’s how qualification management plays a role:
- Automated Certification Tracking: The LMS should automatically track the certification status of learners, including expiration dates and recertification requirements. For example, in healthcare, employees must renew certain certifications periodically. The LMS should notify learners and administrators when renewals are due.
- Compliance Reporting: For companies in regulated industries such as finance, pharmaceuticals, or manufacturing, the LMS needs to generate detailed compliance reports. These reports demonstrate that all required training has been completed and that employees are certified to perform their jobs.
- Skill Gap Analysis: The LMS should have the capability to identify skill gaps by analyzing employee performance and qualification data. Based on this analysis, the system can recommend additional training to close those gaps, ensuring continuous professional development.
Learning Paths and Personalized Learning
Learning paths are a critical feature for guiding learners through a structured and coherent educational journey. An LMS should facilitate the creation of learning paths that can be tailored to specific roles, departments, or industries. This ensures that learners receive targeted training aligned with their individual goals and the company’s strategic objectives.

- Customizable Learning Paths: The LMS should allow administrators to design custom learning paths based on job roles, skill levels, or regulatory requirements. For instance, a learning path for a new employee in a finance department might start with introductory courses on company policies, followed by advanced training in financial regulations and software systems used within the company.
- Adaptive Learning Capabilities: While not necessary for all LMSs, adaptive learning uses data to adjust the learning path in real-time based on a learner’s progress and performance. This ensures that learners who struggle with certain concepts receive additional support, while those who excel can move forward faster.
Blended Learning and Multi-Modal Learning Support
Modern learning strategies often combine different methods to cater to diverse learning preferences. Blended learning, which integrates online and in-person training, is becoming increasingly popular due to its flexibility and effectiveness. An LMS designed for CLaaS must support various learning modalities, including:
- Blended Learning Support: The LMS should seamlessly combine e-learning modules with live training sessions, allowing learners to switch between online learning and physical workshops. For example, an LMS can be used to deliver theoretical content online while scheduling hands-on practice sessions in person, making learning more comprehensive.
- Live Learning Integration: The system should integrate with virtual classrooms, webinars, or video conferencing tools to deliver live, instructor-led training sessions. Features such as attendance tracking, participation analytics, and recording capabilities are necessary for managing and accessing these sessions.
Reporting and Analytics
A critical component of an LMS is the ability to generate detailed reports and analytics. These insights help administrators monitor the effectiveness of training programs and identify areas for improvement.
- Custom Report Generation: The ability to create custom reports based on specific criteria, such as departmental performance or compliance with training requirements, is essential for tracking progress and meeting external auditing needs.
- Data Export Capabilities: The LMS should allow data export in various formats (e.g., CSV, Excel) to integrate with other business intelligence tools or CRM systems, ensuring seamless reporting and data management across the organization.
5. Automation and Personalization of Learning Content
Automated Administration: Automated notifications and certification reminders reduce administrative workload and ensure that learning processes run more efficiently. For example, companies can ensure that employees complete their compliance training on time.
Learning Analytics and Optimization: Detailed reports on learning progress enable companies to monitor and continuously improve the effectiveness of their training programs. For instance, a company may identify weaknesses in certain courses and make targeted adjustments.
6. Operationalization of the CLaaS Business Model
Automation and Self-Service: Self-service functions within the LMS allow companies to manage their training programs largely on their own, reducing the administrative burden on the service provider and increasing efficiency.
Efficient Service Delivery: Automated onboarding processes and standardized workflows enable quick integration of new clients into the system and timely provision of training services.
7. Challenges and Risks
Implementing a CLaaS model involves several challenges, particularly related to technology and regulatory compliance.
Technological Challenges: The platform must be flexible and secure enough to meet various customer requirements while maintaining high security standards. This is crucial for protecting sensitive data.
Regulatory and Legal Requirements: Compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR and industry-specific regulations is an ongoing challenge. Regular updates and audits are necessary to ensure adherence to these regulations.
8. Conclusion
Corporate Learning as a Service (CLaaS) offers companies the opportunity to maximize their internal training resources while generating new revenue streams.
The foundation for a successful CLaaS enterprise is a robust and scalable Learning Management System (LMS). An effective LMS must be highly customizable, adaptable to the needs of different industries, and capable of delivering white-label solutions. Additionally, it should integrate seamlessly with existing business systems and support a wide range of learning methodologies, from blended learning and learning paths to qualification management and comprehensive reporting.
The LMS acts as the backbone of the entire training operation, enabling companies to provide robust, personalized, and compliant training programs that cater to both internal employees and external clients. With the right LMS, CLaaS becomes not only a viable but a profitable and sustainable business strategy in today’s increasingly digitalized work environment.
Source: *Global Market Insights, 2022: E-Learning Market Size Report

About Us
Since 1998 SoftDeCC is working closely with major training centers and academies. This results in a unique experience with training requirements.
Our Learning Platform is designed to adjust to individual corporate learning processes and address evolving challenges. More...

Contact us for more Information
We are looking forward to sharing our experiences with you.
Call +49 (0)89 / 3090 839 30 to arrange for your free consultancy appointment.
.webp)




