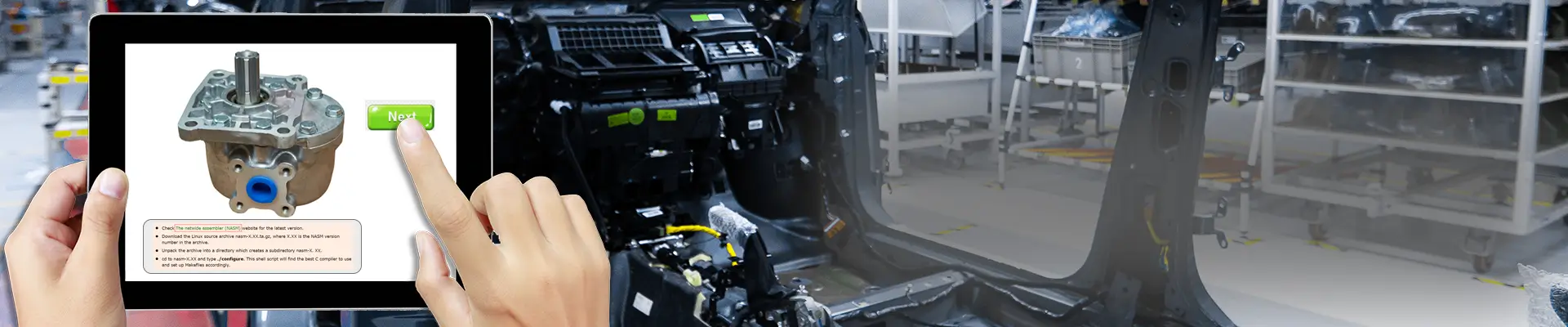
Product Training - Success factor for Industries
Personal development and training for dealers, technicians, and customers are becoming increasingly essential for the success of a company. Training programs not only need to be designed in terms of content and teaching methods but also organized and evaluated. Professional seminar management and qualification tools, training portals, and learning platforms support these efforts.
Product training is crucial for sales and service personnel to emphasize competence and the quality of complex products. Up-to-date product knowledge is indispensable for fulfilling service contracts, which often include maintenance and machine care. Knowledge transfer and competence are the building blocks for extending customer relationships, as they prolong the product lifecycle and intensify customer loyalty. This leads to repeat purchases and, in turn, increases revenue.
Customers who feel well-informed and perceive you as a competent partner are more likely to be available as reference customers. When developing or introducing new, complex products or equipment, training sessions can also help identify customer preferences and opinions.
Well-informed and trained maintenance, service, and sales personnel are more satisfied and establish a personal connection with customer companies. High-quality product training can reduce their turnover rate.
Staff trainings impact on Company Success
The qualifications of employees significantly determine a company's success and its potential for innovation, and they hold substantial strategic importance. Knowledge, skills, and the willingness to continue developing form the foundation of all change processes, technical innovations, and the implementation of new developments in the market. The Laboratory for Machine Tools and Production Engineering (WZL) at RWTH Aachen estimates the level of automation in the German manufacturing industry to be an average of 79%. (1) This indicates high demands in terms of maintenance, availability, and resource planning. Furthermore, the partly intense competitive pressure necessitates strategies for differentiation in the market.
The obvious lever in this context is not only in product design, i.e., functionality and application scope, but demonstrably in service. This includes both the support of implemented solutions within the framework of updates and maintenance contracts, as well as customer service through sales and service branches.
For all of this, product training, meaning familiarity with and knowledge of the company's own products, is essential. Employees, especially those in sales and service partnerships, are drivers and multipliers of the company's success. Training in various areas such as compliance, security, etc., not only complies with legal requirements but is also undeniably necessary to gain a competitive advantage. Companies need coherent and strategically aligned concepts for how to sustainably develop the expertise of their specialists, retain it within the company for the long term, and make it accessible to the right employees. (2)
 Importance of Infrastructure
Importance of Infrastructure
Infrastructure for comprehensible and reproducible training management must be supported by suitable IT, especially a professional Learning Management System (LMS) and training concept.
This fact and the practicability of an IT-Solution is regarded as being highly significant for training management.
Still there is an enormous potential for improvement. Forty percent of all applicants for the German Education Award (Deutscher Bildungspreis) claim to have appropriate software. Closer research showed that these solutions were not sufficient.
Only 16.9% declared that they were operating a software to track competences and qualifications of their staff. The small numbers of suitable IT-support (37%) indicate that the enormous potential, of professional IT-tools in training management has not been sufficiently recognized yet.
Enhancing Efficiency in Sustainable Operations
Sustainability, particularly in the realm of maintenance, extends across technological, economic, ecological, and social dimensions. The realization of diverse concepts hinges on the indispensable role of individuals as bearers of knowledge. Within the spectrum of availability management, judicious resource utilization emerges as the key to sustainable efficiency gains. This approach not only curtails energy and raw material costs but also fosters environmental and economic responsibility. (6)
Integral to the successful implementation of various processes—be it in sales, maintenance, or technical services—is structured knowledge transfer. The interconnectedness of sustainability, knowledge, and learning underscores the importance of behavioral shifts, such as adopting novel maintenance or communication processes, mastering new techniques, and more. Predominantly engaged under service contracts, maintenance specialists become linchpins in the pursuit of sustainability.
For manufacturers and service providers seeking a competitive edge through optimized maintenance scenarios, the emphasis lies in preserving and nurturing the expertise of their employees. Ongoing training and education become imperative to achieving this goal (7), without causing disruptions in availability. As echoed in observations, the reservoir of knowledge in maintenance personnel's minds far outweighs what is documented on paper or processed in data formats." (8)
Multipliers of Company Success
Employees, especially sales and service partners are multiplier of enterprise success. Trainings in manifold areas such as compliance, security issues are not only following legal obligations, but are also necessary to control sustainable development in corporations. Companies require clear and logical concepts to develop the knowledge of experts, keep this knowledge in the corporation long-term and make this knowledge available to the right staff members.
Infrastructure for comprehensible and reproducible training management must be supported by suitable IT, especially a professional Learning Management System (LMS) and training concept. This fact and the practicability of an IT-Solution is regarded as being highly significant for training management.
Still there is an enormous potential for improvement. Forty percent of all applicants for the German Education Award (Deutscher Bildungspreis) claim to have appropriate software. Closer research showed that these solutions were not sufficient. Only 16.9% declared that they were operating a software to track competences and qualifications of their staff. The small numbers of suitable IT-support (37%) indicate that the enormous potential, of professional IT-tools in training management has not been sufficiently recognized yet.
Revolutionizing Maintenance for Sustainable Success
Sustainability within the maintenance domain encompasses technical, economic, ecological, and social perspectives, with human involvement as the linchpin of bringing these facets to life. Elevating efficiency sustainably involves enhancing the quality of availability management for machinery and installations, translating into reduced energy and raw material costs.
Maintenance specialists, commonly operating within service level agreements, play a pivotal role. Vendors and service providers aiming for improved maintenance settings must leverage the expertise of their staff. Specialized further education becomes a catalyst for cultivating this expertise, ensuring service remains uninterrupted. Emphasizing the significance of expertise residing primarily in the minds of service staff, the importance of documented knowledge cannot be understated.
At the 'Maintain' show in 2007, Professor Dr. Kalaitzis outlined the distinctions between sustainable maintenance concepts and traditional cost-cutting approaches. The transformation of enterprises into learning organizations is imperative for efficiency gains in maintenance processes, as evidenced by reduced downtimes through controlled maintenance cycles and sophisticated availability management.
 Hands-On Product Training
Hands-On Product Training
To increase efficiency within the maintenance processes it is imperative to transform the enterprise into a learning organization. It is not a secret, which controlled maintenance-cycles and sophisticated available management lead to decreased downtimes.
Availability is supported by up-to-date knowledge of staff. When the availability and quality of knowledge is unknown or concentrated to only few people, a permanent quality level cannot be guaranteed. Even the best technical staff cannot be sufficiently prepared to manage complex installations’ updates or release changes without special training.
The more technology develops towards Industry 4.0, the more critical up-to-date maintenance Know-How is required for entrepreneurial success.
Evolving Perspectives on Corporate Sustainability
In 2003, only 40 percent of all enterprises and 54 percent of DAX corporations considered sustainability a critical issue. Fast forward to 2011, where more than two-thirds and over 90% of all DAX corporations now proclaim sustainability as a highly relevant factor for their future development.
Drawing parallels between the DowJones Sustainability Index and the MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International), these indices, reflecting 10 percent of enterprises meeting specified sustainability criteria, illustrate the interconnectedness of economic and ethical actions. Empirical studies by Professor Dr. Uwe Hannig and Philipp Tachkov affirm that sustainable management is not only ethical but also lucrative, highlighting its potential for long-term success in the evolving landscape of Industry 4.0.
Product Training in Sales
Transaction cost theory states that it is impossible to finalize negotiations in one go. As a rule, contracts are continually renegotiated and readjusted. This is particularly true for complex industrial goods such as software. To limit the costs and risks of all parties the existing, proofed and assumed knowledge of the product is significant. Indicating sustainable product training is therefore not only mandatory for the initial negotiations and sales presentation but also the transfer of knowledge from producer, sales and service staff to the customer must not be spared. This is mandatory as the customer lifecycle expands with perceived quality of service and communication; that is from first contact from initial installation through service updates parallel to customer communication along the process of fulfilment.
Higher customer satisfaction increases and facilitates reselling, up-and cross-selling. Increased knowledge concerning particular customer requirements can only be detected by continually employing up-to-date service staff, likewise, increasing the customer value due to the fact that the effort for new projects decreases. At the same time less of the enterprise’s resources are required to differentiate from competitors. The longer the customer-provider relationship lasts the lower transaction costs are, due to communication at eye level.
 Customer Contact
Customer Contact
Regular product trainings of internal and external sales and service staff strengthen the brand not only by perfect technical knowhow but also the brand must be considered trustworthy and of quality.
This feeling of minimal risk and trust is transferred nonverbally during contact with prospective customers and therefore underpins the service to be expected concerning competence and customer orientation which are both significant points of differences in competition.
Transaction cost analysis suggest that lacking or incomplete training causes uncertainty also in respect of maintenance of machinery and equipment, but also of the knowledge and competence of the technical sales force.
This results in higher cost for sales and will also effect prospective customers and vendors.
Consumer acceptance and Insecurity of Enterprises
There is sufficient proof and it is logical, that a successful introduction of products depends on the evaluation of the obvious advantages of a product in connection with its cost and in relation to the relative advantages of a competitor’s product.
To sell complex products and innovations without being familiar with them, it’s usually the case that the potential for future development is in fact also a mental and emotional problem, not only for sales and service but also for a prospective customer; trust lost due to lack of competence or product knowledge can hardly be regained by investments in advertising and PR.
Checking back with details especially for technical specifications are inevitable to smooth out uncertainty. As an example, for complexity of purchasing on one side and resulting sales tasks for investment goods it’s better to carry out a survey concerning uncertainties during a software procurement process can be employed. After uncertainty concerning software quality and changes of company structure due to new software the qualification of users and administrators ranks third.
This finding can be easily transferred to investments in engineering and construction, service robotic and other sectors. “Before implementing new products, technologies or procedures staff have to be prepared thoroughly. Employees have to be trained to deal with new complex systems and innovations to deliver best performances and services based on new processes themselves.
 Production and Maintenance
Production and Maintenance
To cope with new tasks or equipment, and to reduce or eliminate mentioned uncertainties as described previously, sales, support and service staff must be trained extremely well. The service offering containing respective training programs for users and administrators is therefore an important part of the service portfolio and mandatory point of difference in competition.
Sending a whole group of experts of different professional backgrounds for initial negotiations may demonstrate a high level of the vendor’s expertise, but at the same time illustrates complexity and potentially the high maintenance level the plant or unit may require as well as a potential dependency on the know-how and support the vendor is providing.
Rogers has identified complexity as such as an aspect of successful product implementation. T
he E³-Model (expectation → emotion → evaluation) shows a definite connection between expectations of complexity, resulting uncertainty and finally a rating of the product already at market introduction. The further uncertainty can be reduced by sound product knowledge, the higher the efficiency and thus the profit ratio of the parties involved. Acceptance within the own corporation is mandatory as it serves as the basis of transferring the perceived product-and service quality to the customers mind and is therefore the minimum basis for increase in market share and turnover.
 Motivated Team
Motivated Team
The more uncertainties can be reduced through well-founded product knowledge, the more efficiency and thus the profitability of the business relationship between all parties increases.
The acceptance of new products within the company is the foundation for transferring the perceived product and service quality to the end customer, and thus the basis for market share and revenue growth. Training sessions can also serve as a platform for introducing or promoting new products or as test scenarios for professionals under manufacturer-controlled conditions.
To enhance the quality and accepted brand value, intensifying product knowledge and sales arguments for already established products is just as important as the introduction of innovations.
However, training for field sales representatives and external service partners is not solely for informational purposes but can also be used for motivational purposes. The company's interest is to increase the acceptance of field sales representatives for new products. The contact also enables a closer bond with skilled professionals within the company.
In Touch with Customer and Market
Providing trainings offer another communication channel between customer and vendor. Trainings, especially questions asked to disclose a sincere customer feedback concerning expectations, typical technical problems when bringing a plant into service. Furthermore, suggestions and wishes for improvements from technicians, intermediaries, and end customers. The respective knowhow is influencing the operating time between failures, total service cycle and availability management including maintenance cycles.
The pure installation of plants, machinery, or implementation of software as such is usually not a satisfactory start for flawless operation and maintenance. Obviously well-trained staff is enabling the corporation to be productive earlier. This way cost during the implementation will be minimized and a return on investment can be generated faster. It is not without reason that complex machinery comes with a variety of service contracts. Still thoroughly constructed training programs for operators are mandatory to guarantee maintenance during shifts and enabling repairs of minor incidents. Trainings to avoid user mistakes also apply for changes of release and modules or changes in the location. User failures are critical as they have a high impact on customer satisfaction.
Repurchases and replacements, service contracts as well as the possibility of satisfied customers serving as positive references are influencing the development politics of a vendor to a high extend. Each order means a serious, partly also a sine-qua-non investment decision.
 Trust
Trust
Maintenance and services including trainings will therefore always be integrated in investment decisions. Incomplete knowledge transfer resulting in unsatisfactory maintenance cycles, early recognition of problems and danger as well as safety precautions can also be also legally enforced. Thus, training contents as well as training quality must be ensured and proofed by appropriate tools and certified to meet legal, contractual and insurance requirements (Compliance).
Trainings at all levels must be integrated properly in the business strategy and are therefore especially relevant for sustainable customer relations. Hands-on training concepts are only efficient if the infrastructure as in software, processes and company culture supports them accordingly.
Like supply-chain-management structures web based LMS and training administration software can deliver solutions for cross-company knowledge solutions. Transparency and information transfer as well as quality and efficiency of trainings processes circle round an integrated partner management. Protected learning portals offer individual possibilities to the relevant target groups such as trainers, staff, HR and managers) to share advantages and cost of such a system and increase efficiency at the same moment.
There is no single answer to the question if customers are to contribute to training fees, the trainings come as a part of the service contracts or if single corporations are sharing a percentage of the cost. This is a highly individual decision as this is resulting from the strategic direction of the individual business model.
However, a Learning Management System must be able to serve all the respective requirements. Customer value analysis can inspire different solutions for different partners, no matter if those operate complex plants in solution management, software, or service robotics.
Structured Corporate Learning
Learning Management Systems (LMSs) today manage knowhow-transfer cross time and location. Sustainable product trainings achieve not only knowledge and competency. Independent from the product life cycle they support in long term customer relationships. Therefore, an efficient organization of training management is the basis of short and long term success of a company not only during later maintenance but already during acquisition and implementation.
The basis to achieve this is by use of a proven and tested training administration software. Not only support of academies and HR-development concerning training organization as such is essential. As tasks and involved roles in training organizations manifold a suitable LMS offering services to all parties is seen as a major quality characteristic for customers and partners.
To enable your own sales and service department or your partner’s staff to choose and enroll online in suitable courses as well as the integration of individual reporting and approval structures are key issues to a close cooperation across companies or business units. Due to the fact that training programs developed over the course of time consist of various components (e.g., classroom training, course chains, WBTs, Chats, assessments, video lectures or virtual classrooms) an LMS nowadays must bear an integrated approach.
Participants and users must be able to make fast forward choices in their operation paths without restricting them or forcing them to logon several times to several systems. Still, they must be able to keep track of processes and continue seamlessly even if on demand tasks divert their attention.
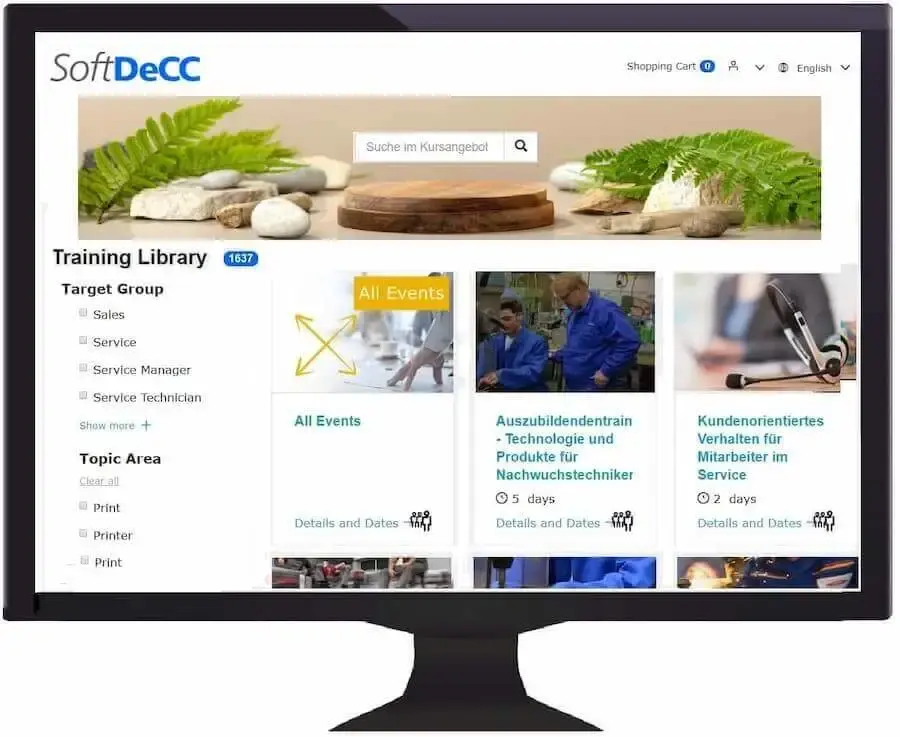 Training Catalogue
Training Catalogue
The planning of training measures often fails in advance due to the constraints and contingencies of practical business operations. "Open" booking concepts have proven to be effective, where potential participants first inform themselves about suitable training options in terms of content, location, and time through web access (participant and dealer portals) and then register.
In the case of web-based learning content and tests, they can sometimes be initiated immediately. Upon completion, certificates and participation certificates are available for download.
Training Administration Software
The ‘static’ administration of training might be operated by an industrial academy or oversee the HR or personnel development department. Courses and dates but also career and qualification paths for an individual person e.g., a technician of a subsidiary, staff of a customer or own service and sales force are planned and administered. Learning progress and knowledge acquirement must be tracked, updated and documented with minimal effort.
Training management systems (= course management software) administer a broad variety of training types. Classic classroom training, download of supporting information, web-based training entities (WBTs) can be managed as well as date sequences or curricula which are made up of diverse types of training units (Blended Learning).
Also, if knowledge has been acquired certain persons such as shift-or workshop managers must be able to track down fast who in their team has certain qualifications, especially in case of sudden repairs or operations. A high volume of special qualifications must also be continually renewed due to legal or insurance demands.
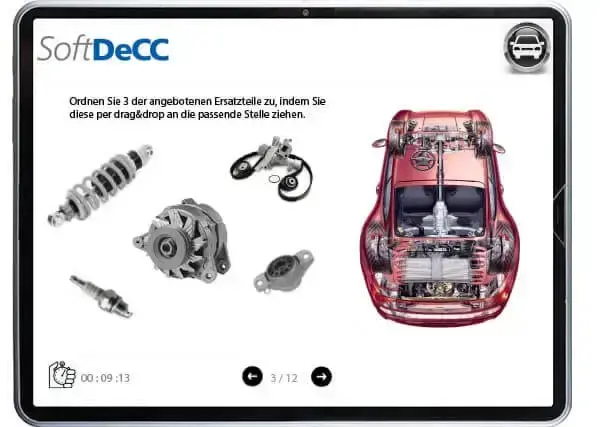 Online-Test
Online-Test
One way is to add time stamps to certified knowledge (test results) and configuring the training management system to set off an indication when an update or recertification is due for a particular member of the crew.
If different locations or subsidiaries are involved entitled staff such as a branch office manager must be enabled to draw reports and training histories featuring the knowledge status of their personnel. The required accuracy can only be granted by employing professional training management software.
Processes must be configured individually for any corporation. If training cycles are set up accordingly and adjusted to maintenance routines specialized and certified staff will maintain services at customer’s plants and profit from trust generated by quality services.
 Instructor-led Training
Instructor-led Training
Reports should be accessible from the training center, as well as from authorized personnel or branch managers, listing the current or imminent training needs. This can only be achieved with software that can access the up-to-date data at any time and can be configured individually for the company's processes. It may also be desirable to acces the information in other applications and design appropriate interfaces.
Ideally, the current knowledge level of an employee is combined with a resource allocation tool. As a result, it ensures that the customer's trusted maintenance staff are always well-informed and well-trained. The familiar and competent personnel also benefit from customer trust. This further strengthens the relationship with the customer.
Trainings portals and learning platforms
Training portals serve as access points for various stakeholder groups to the manufacturer's learning platform. Different access levels for administrators, instructors (trainers), HR personnel, and, of course, learners offer various options for managing, delivering, acquiring, testing, and tracking knowledge and skills.
Depending on the roles and permissions structure, technicians can either independently enroll in courses or initiate an approval process through a booking request. In this routine, their supervisor and/or the training office can quickly grant consent with a few mouse clicks, triggering binding reservations. Branch managers of service and sales branches, as well as external partners, can create their own employees in the Learning Management System (LMS) through their secure access, thereby initiating qualification processes.
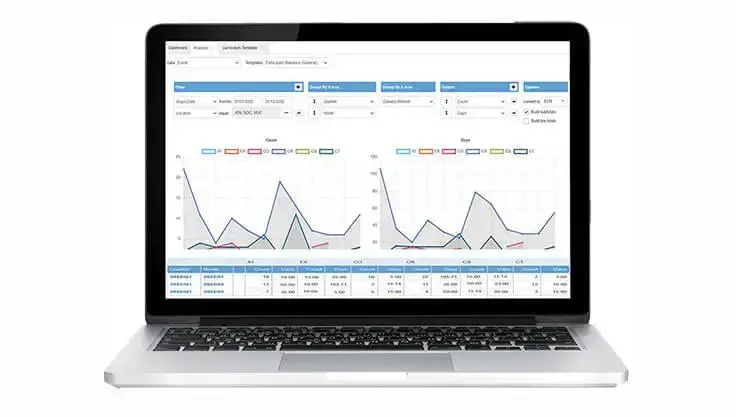 Training Statistics
Training Statistics
A sophisticated reporting system provides information about training status, educational history, and career paths. In the personal training areas of employees, not only can courses be booked, web-based trainings (WBTs) be initiated, and tests for knowledge assessment be conducted, but also the quality control of training can be carried out using predefined questionnaires, even after longer time intervals (‘transfer feedback’ if needed).
These responses can then be analyzed by the training center at a granular level, i.e., on a question-by-question basis as well as by question categories. This helps identify optimization potential, and improvements can be implemented based on the specified priorities.
Conclusio
Structured knowhow-transfer is a mandatory prerequisite for successful implementation of processes and concepts of all kinds, independent if sales force or maintenance crew are involved. Denominations such as sustainability, knowledge and learning are inseparable as changes in ways such as new maintenance or communication processes, modern technologies etc. can only be employed and exploited by adopting series of cognitive and practical activities.
Trainings are also a platform for introducing new products or for testing interest and reactions of business partners under controlled circumstances. Trainings can expand the customer life cycle, initiate repurchases and acquisition of further products and services.
To increase and monitor quality and thus maintain brand value by intensification of product knowledge and therefore increased identification of customers and own staff likewise. Especially trainings for external service staff and sales force do not only serve as knowhow and information transfer but are also essential motivational tools. The acceptance of new products not only increases turnover. The continuous contact with decreases the fluctuation of a highly qualified workforce.

About SoftDeCC
Since 1998 SoftDeCC is working closely with major training centers and academies. This results in a unique experience with training requirements.
Our Learning Management System is designed to adjust to individual corporate learning processes and address evolving challenges. More...

Your free Consultany Appointment
Discuss your learning Challenge with us.
Call +49 (0)89 / 309083930 to arrange for your free consultancy.
Sources
1. Diehl, Hans-Jörg. 2000.Marketing für betriebswirtschaftliche Standardanwendungssoftware. Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien, 2000.
2. Dreyer, Anne. 2013.Qualitätsmodell betrieblichen Bildungs-& Talentmanagements. Bildungs-& Talentmanagement. München: Hrsg.: EuPD Research Sustainable Management GmbH, TÜV SÜD Akademie GmbH, 2013.
3. Enste, Dominik H.Lohnt sich Nachhaltigkeit? [Online] Institut der deutschen Wirtschaft, Köln. [Zitat vom: 13. 5 2014.] http:/ /www.iwkoeln.de/de/infodienste/wirtschaft-und-ethik/beitrag/53199.
4. Hanning,Uwe und Tachkov, Philipp. 2011.IMIS. [Online] 2011. [Zitat vom: 13. 5 2014.] imis.de/portal/load/fid816043/Studie%20zur%20nachhaltigen%20Unternehmensf%C3%BChrung.pdf.
5. Kalaitzis, Dimitrios. 18.10.2007.Nachhaltig erfolgreiche Instandsetzung. Messe: Maintain-Europe: s.n., 18.10.2007.
6. Kuhn, Axel und Schnell, Marcus. 2001.Instandhaltungswissen besser nutzen -strategischer Faktore für den Unternehmenserfolg. [Buchverf.] A. Hrsg. Kuhn und G. Bandow. Wissensmanagement im Expertennetzwerk. Dortmund: Verlag Praxiswissen, 2001.
7. Moreau, C. Page, Lehmann, Donald R. und Markman, Arthur B. 2001.Entrenched Knowledge Strucures and Consumer Responses to New Products. Journal of Marketing Research. 2001, Bd. 38.
8. Ouchi, W.G. 1980.Markets, Bureaucracies and Clans. Administative Science Quarterly. 1980, Bd. 25.
9. Picot, A. 1982.Transaktionskostenansatz in der Organisationstheorie: Stand der Diskussion und Aussagewert. Die Betriebswirtschaft. 2, 1982.
10. Rogers, E. und Singhal, A. 1996.Diffusion of innovations. In Salwen and Stacks op.cit. S. 409-420. 1996.
11. Schemat, Jörg. Bonn / München.Fachwissen nachhaltig entwickeln. Bildungs-& Talentmangement -Jahrbuch 2013. 2013: Hrsg: EuPD Research Sustainable Management GmbH & TÜV SÜD Akademie Gmbh, Bonn / München.
12. Schuh, G., et al.2005.Intelligence Maintenance -Potenziale zustandorientierter Instandhaltung (Abschlussbericht). Aachen: s.n., 2005.
13. Wanizcek, Mirko und Werderits, E. 2006.Sustainability Balanced Scorecard. Wien: LindeVerlag, 2006.
14. Wichlajew, A. 2007.Nachhaltige Instandhaltung -Schlagwort oder Erfolgsrezept? München: AKAD Privathochschulen, 2007.
15. Wood, Stacy L. und Page Moreau, C. 2006.From Fear to Loathing? How Emotion influences the Evaluation and Early Use of Innovations. Journal of Marketing, American Marketing Association. 70, 2006.





