What does digital transformation mean for corporate learning management?
Digitalization is everywhere. Keywords such as "Industry 4.0", "Disruption" and "Automation" are broadly discussed and cause all emotions from euphoria to fear. Digitalization does not stop before training centers and personnel development. On the contrary: HR and staff development can be central drivers of a successful digital transformation.
But what is behind all this? What can we expect and what prerequisites must be met to deal successfully with the anticipated changes?
The Challenge
According to Wikipedia Digitalization means mainly the "Change towards electronically supported processes by employing information and communication technic". This aspect seems slightly anachronistic if you apply it to operational practice. Especially in Corporate Learning, Digitalization is much more than mere software support, as enterprises are sociotechnical constructs entail far more than process organization.
Implementation of digital leaning landscapes support operational practice far more than the integration of formal and informal learning scenarios. Modern Blended Learning Management schemes include individual learning and qualification paths. They are designed, so qualified professionals can develop themselves in the best possible way. This results in a higher identification with the tasks and the enterprises, so retention spans are longer. And last but not least; appropriate, individual learning concepts result in better application to practise and therefore to a higher Return on Education (ROE).
The Task
Targeted support of individual learning paths is a complex matter. It is easy to understand the manifold challenges of staff developers and instructors. Not only have they to create suitable qualification paths for the employee and his/her tasks and develop them under consideration of corporate strategies.
Modern educational management also requires appropriate content for different learning types to be available in various formats.
 Various Learning Formats
Various Learning Formats
This multimedia approach is to be enhanced by collaborative formats supporting the theory-to-practice experience. Media and responsive content must continually be updated to recent developments by professionals (curation). Also exchange of learners across platforms might require moderation. Relevant comments and feedback should be integrated in the next curation cycle. And qualification campaigns should be accompanied by education controlling (and improved accordingly with each iteration). SCORM-tracking and Learning Analytics are supporting educational controlling but must be integrated according to corporate philosophy and requirements of the works council.
Going by the multitude on tasks and complex interactions it is not surprising, that LnD-Staff must be relieved of routine work, so they can concentrate more on their value-adding tasks.
New technologies and an increasingly higher degree of automation promise to relieve HR and LnD from routine tasks. But it is not a mere question of special software. A highly developed system integration results in the connection of various IT applications via interfaces.
This enables Data exchange between the LMS (Learning Management System), HR (Human Resource Management Software) and workforce planning always ensures the appropriate deployment of appropriately qualified staff. Transparency and up-to-date data also increase transparency and support fact-based decisions.
But are corporations as socio-technical constructs ready for this?
Digital Skills
The goal of digitalization in corporate learning is to achieve:
- an higher ROE (Return on Education) and
- to support corporate goals more efficiently by optimized IT-supported processes and increasingly better individual qualification projects.
The added value of digital transformation and the identification with the "project digitalization" is only .tangible to the single employee, if he/she has the relevant digital skills and knowledgte to comprehend the issue and it's consequences.
But what are digital skills? How are they developed and implemented within a corporation?
(Click here to learn more about digital competencise)
What are digital skills?
Talking about digital skills usually results in rather vague statements of what digital skills are. If enterprises today hype " exchange and collaboration" as digital skills, you might be tempted to ask if these were irrelevant in their analogue business. You might also feel doubtful if the "digital skill" web-development is relevant to all positions within a digital enterprise and so is the "dealing with mobile devices".
The latter is especially questionable in corporations with IT regulations lacking information about the issue, where a BYOD (bring your own device) policy does not exist, or IT regulations have not be adjusted to digital transformation. The mentioned points may sound populistic but serve to illustrate that digitalization strategies have to be coordinated with individual corporate realities.
(Learn more about corporate learning strategies)

Examples for digital skills:
- Knowledge of data security and data protection
- qualified to analyse, interprete data for reporting
- media skills
- software skills
- communication skills / dialogue orientation
- innovation skills: recognize and use change
- readyness for continuous growth and development
- responsibility / decision making
- structured work
- process-, project and organizational management
What digital skills are relevant?
What digital skills are relevant to a corporation and to which degree will be a matter to be answered individually. Task profiles and corporate strategy will provide valuable insights when it comes to developing a corporate educational strategy and deduct appropriate qualification paths.
Just like with "eLearning" and "LMS" there is a variety of interpretations and ideas, what the terms "digital skills" and digitalization actually entail. It is necessary to develop a common understanding concerning their meaning and resulting consequences. Only then you can think about how to support, develop and measure them.
Degree of Digital Maturity
This connects seamlessly to the question of the degree of digital maturity (= degree of digitalization). This is less of an KPI indicating how much percentage of processes are automated or supported by IT applications.
The degree of digital maturity describes the process of the strategic discussion concerning digitalization issues.
Core Questions of Digital Maturity

The undisputed core questions of digital maturity are:
- How well are enterprise and staff prepared for the challenges of digitalization?
- How well is made use of the advantages or technical possibilities?
- Have employees the (now and in future) required digital competencies and to what extend?
Media, Formats and Processes
The multitude of terms and their use calls for a differentiation.
Many terms and developments circulate concerning digitalization and are discussed - to some part critically, to some extend passionately. Thus, it seems important to start with a first differentiation what digitalization means for corporate learning.
The declared goals of digitalization in general, but also concerning personnel development and LnD, are an increase of efficiency and an improvement of economics of the enterprise.
Wikipedia (4) sees two general directions:
- a) a "transition of analogue values in digital formats e. g. recording of data" and
- b) "change to digital supported processes by information and communication technology."
For staff development and corporate learning this means the creation and recording of digital learning content, the structured distribution and according to digital communication, proof of training and workflows, always respecting data security and GDSR-compliance.
State of the Digital Art
Corporate Learning today
How does corporate learning actually work today?
In May 2016 the association Bitkom e. V. published a representative research (1), stating that enterprises today increasingly employ blended learning concepts. Digital content as WBT or Webinar is a important part of online-training programs and is combined with external classroom trainings, inhouse events with external instructors and own training staff. But blended learning does not mean a mere substitution of conventional training by electronic based media. Blended learning will be successful if advantages of different media and formats are combined in the most productive way.
Mobile Learning - not an issue?
According to Bitkom mobile learning formats such as interactive ebooks, smartphones or tablet apps have been largely discussed, but hardly implemented. Same applies to Serious games or the offer of online-universities and external learning platforms [Research is from 2016 = pre-pandemic, Covid 19 might have caused changes since]. The research does not give any reasons, but it is to be assumed that it is at least to some extend a question of resources. This implies not only the cost of designing a WBT, but also of contend curation.
"Digital overload in everyday work" (also from 2016 by Sopra Steria Consulting (2)) is gives more interesting insights. Even though the age group of under 30 years is more affine to digital media and technically versed every fourth of those digital natives feels overwhelmed by the speed of the digital transformation. The flood of information inhibits the completion of tasks. The knowledge that a high degree of digitalization is necessary to survive in competition, creates additional pressure. More experienced staff, the so called "digital immigrants" seem more apt to deal with the pressure.
Independent from their actual field of responsibility not only professional competencies must be available when dealing with digitalization, but also methodical competence and softskills to achieve the desired increase in efficiency.
Increasing necessity of Individual Support
For HR, LnD and staff development this is only a confirmation. Individual training offer, personalized content and optional coaching are a must, to let qualified staff fulfill their complete potential.
The resulting identification with the corporation and its goals result in long retention periods. In times of skills shortage certainly a factor that can't be ignored.

The required type of corporate culture places the development of staff in the center of attention. The personal, individual support by talent management, career paths and coaching are a huge challenge to LnD and HR. Individual attention, creation of highly individualized learning content in various media formats are challenging to the resources.
On a cognitive level the necessity has already reached conventional HR management. The actual implementation is often behind the possibilities.
So, what can staff development, corporate learning and corporate training centers together with managers actually do to deal successfully with the change?
These new demands and requirements change job profiles and create new. In corporate education tasks like content creation / curation in various media formats and the (digital) management of target groups (e. g. community management) gain relevance.
Another aspect is the support of staff by appropriate software support. Automation of processes and connected system landscapes with user-oriented surfaces must provide the appropriate functions to assist individual tasks.
Support by appropriate IT
System Integration
System integration relates to the technical connection between different platforms and software applications via interfaces. Interfaces serve the data exchange between different software applications (LMS to HR, Finance...) so identical, up-to-date information is available in different departments.
For example: staff deployment might only be able to assign an employee with a certain valid qualification. If a qualification is due for periodical refreshment the staff member and/or manager will be informed by the learning portal or in a report. A connection of this requirement to the training catalog triggers an enrollment-, approval-, invoicing- and communication process involving the academy, an instructor, finance and HR. If the training cycle has been completed with e. g. a test or a certification the respecting information is distributed in all relevant systems as well.
Systems integration can lift specialized software and platforms to a new level of efficiency.
Potential of automation
Automation can ensure a frequent synchronization of data in different systems. Automated processes can trigger or execute next steps. The questions result, on what basis automation is defined, what the requirements for automation are and when automated processes make (no) sense.
Advantages of automated processes are obvious and have been discussed on great length:
- up-to-date data (near real time)
- process acceleration
- reliability
- traceability
- standardization, reproducibility
- efficiency
- ....
Limits
Automation is not making human contribution obsolete. Especially where people are involved, machines cannot be trusted to command individual or spontaneous decisions and exceptions. Interpretations of data based on extended cause-and-effect-analysis, appropriate reactions to unforeseen occurrences, changing or complex task, cannot be left to robots. Other examples for the limits of automation are the evaluation of team dynamics, critical thinking and development of concepts, semantic interpretation, appropriate flexibility, and intuitive reactions.
Of course, nowadays advanced AI (artificial intelligence) programs can recognize emotion and facial expressions based on learned algorithm and respond to them. But this is not equal to human empathy.
Especially with sensitive issues automation can be interpreted as demonstrative ignorance. Possibly a corporate culture like that shows remaining staff their status. It must be considered carefully, where automation offers added value and relieves staff from routine tasks and pressures and where humans should make decisions and act.
Checklist: Automation
- How much automation really improve my achievements?
- For which business area is automation an improvement?
- Where might automation makes more difficult or block my daily business?
- When does it cost more than it helps?
- ...
Frequent arguments against a complete automation are:
- sometimes tedious adjustment processes (machine learning takes time and requires lots of data)
- costs, resources
- possibly not sufficient knowhow
- possible loss or reduction of flexibility
Furthermore, you are to consider legal aspects of automation e. g. concerning liabilities, as well as ethical and social aspects. It is not to be underestimated how automation influences corporate culture and style.
The Value of Corporate Culture
A successful digital transformation requires not only software support, but also a suitable - digital, but not un-personal or even non-personal corporate culture. People are central success factors in enterprises. Humans in general want to contribute opportunities of development, empathy and appreciation. Robots, machines and automatons can at best simulate those. Digital skills are necessary to develop a digital-human corporate culture and this development hast to be shaped by HR, organizational development (people & organization) and Corporate Learning.
First you will require a roadmap, that is conceptional evaluation where in the enterprises routine tasks take up time and can be delegated to machines in order to free qualified staff up for more valuable jobs.
Within HR the workload shifts from administration to individual consultancy and personal attention. This aims to raise the quality level of employees work, their motivation and identification with the corporation, resulting in longer retention spans. The integration of corporate culture in goals and strategy is not only an important lever, but also a real investment in the brand, a factual raise of the corporation's value.
Success factors: technology, culture, and skills
These success factors equal the action fields to be targeted during digital transformation.
Learning Management Systems - more relevant than ever
"LMSs are dead" at least according to education expert Jochen Robes's book 'Digitale Bildungslandschaften'. It is the nature of general statements, that they are not universally valid.
Modern Learning Management Systems are more important than ever. "Dead" are only the idea of ancient, inflexible island solutions, providing a singular process from authoring to certification. Since then (we are referring to the year 2000) LMS have developed. Some have even seen the necessity to employ new terms such as LXP to avoid the associated stigma.
LMS today are flexible tools and allow for broad configuration to support even complex processes and relieve LnD staff from many routine tasks. Also, the systems integration (some use the term "learning eco systems") is increasingly important. Systems integrations connect various systems and enable a continuous data exchange.

Of course, informal learning is a part of personal and corporate development. This has always been the case. LnD is now more than ever required to enable informal / social learning. For HR and instructors this additional offer results in more demand or their time. This time can be freed up with appropriate software support and suitable automation processes.
Thus, modern Learning Management Systems are economic factors across corporation. Their existence and extent of use might even be seen as a litmus test illustrating competencies and knowledge of the corporation and illustrate the sustainability of the respective company.
LMSs today: flexible and highly integrable
Learning Management Systems today are superior systems which can:
- handle automated processes
- coordinate qualification projects
- Aggregate and evaluate data
- grant secure access of authorized individuals to functionality and data
- provide authorized individuals with correct information
- reliable process support
- be fully integrated in complex system landscapes.
They are independent from particular learning formats, which means they can incorporate informal, social, formal and collaborative learning elements to any conceptional extend (New Blended Learning).
One Solution fits all?
What is true for individual employees is equally true for companies. There is not one solution, which matches all requirements. A rigid 70:20:10 (social - self-organized - formal) for qualification concepts is equally inflexible and goal-oriented like one formal curriculum which is rolled out to all staff members equally.
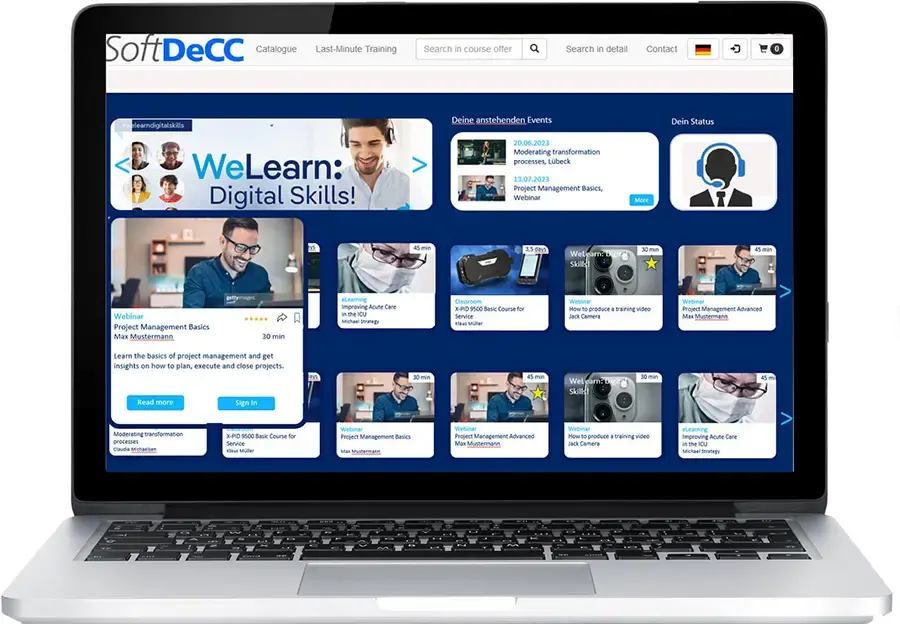 Learning Platform
Learning Platform
For corporate Learning dogmatic universal solutions are not the solution. New ideas and experiments are impulses leading to critical thinking and appropriate solutions.
Enterprises should generally be open to new developments but equally use the advantages of established software solutions to profit from new findings in behavioral economics, psychology and staff development.
Status Quo
Research have proofed, that no enterprise sees itself as a digital champion or perceives its digital process developments as completed. This is good news, as it also shows the corporate reality of your competitors. Many organizations are still on the quest of their digital positioning or busy to consolidate their digital basis. As current challenges the update and modernization of IT-infrastructure has been mentioned.
Companies, which have recognized the scope of corporate learning / LnD regarding digital skills, are implementing flexible systems supporting structured training of appropriate competences, that is modern Learning Management Systems. The particular challenge is to integrate individual learning paths in an overarching, comparable and therefore controllable corporate educational management.
Key characteristic of modern LMS is not anymore, that they integrate all aspects from authoring tool, course management and qualification schemes in one. Today’s LMS grant a high flexibility by their own set of broadly configurable functionalities and the possibility to enhance the system with all applications, which are wanted for a unique and individual learning and qualification system.
This way the individual advantages of partly very specialized applications such as collaboration tools, mobile apps and learning nuggets are centrally integrated, evaluated and distributed according to the individual requirement of learners.
Target-group optimized learning portals grant secure access to sensitive content, personal data and role-specific features. They are seamlessly connected to the LMS (Learning Management System) as a central information hub.
Checklist: Todos in Digitalization
Software support, automation, and degree of systems integration as well as the technical infrastructure are a mere vehicle for continuous increase of efficiency. Success depends on the development of an appropriate corporate (learning) culture. Thus, you must ensure that all stakeholders can develop the appropriate digital skills. Also, in digitalization It is not goal oriented, to put everybody through the same standard courses indiscriminate of the individual challenges.
Software support by learning management systems with a suitable degree of systems integration and automation frees up resources required by HR and academies to deal with individual members of staff. Advocates of digitalization must be aware that digitalization influences corporate culture to a high degree, but corporate culture can also be a big lever to success.

- Assessment of digital maturity
- Integration of digitalization in Corporate Goals
- Conceptional discussion of issue
- Investment in digital infrastructure e. g. Learning Platform, LMS
- Prompt integration of HR / Corporate Academy
- Close cooperation with experienced IT / Software vendors
- Update of IT regulation and processes for the use of new technology
- Adjustment and automation of processes
- Continuous improvements in connection with corporate strategies
- Assignment of responsibilities and budgets
- Design and implementation of education campaigns
- Recruiting of staff with appropriate skills
- Training and qualification of staff for appropriate skills
Conclusion
The good news: it is not too late to start working on the digitalization of your LnD, as no corporation perceives itself as a corporate champion. However, it is high time to consider digitalization concerning corporate learning, academy management or within industrial training centers. In any case you will want to start to invest in your future.
A digitalization process is not completed with the implementation of a software. The definition of a general suitable degree of digitalization is not a suitable solution to an enterprise, HR or employees. Digitalization is a highly strategic issue focusing on own potential, possibilities, and expectations. Without formulating a digital corporate strategy, the required skills for the single departments can hardly be identified, assigned and encouraged.
(Read all about what you need to know about Corporate Educational Strategies)
Thus, digitalization is not a merely technical matter, but closely connected to corporate- and management culture. Essential key to all change projects is communication. All employees must be picked up at their respective stage of their development (5). That is where gap-analysis of their digital and media skills come in. Modern, flexible Learning Management Systems support digitalization projects guided by corporate learning professionals.
A thorough analysis of positioning under consideration of corporate goals is the basis for development of further steps. Employing iterative procedures allows for flexible reaction to developments and occurrences.

About us
Since 1998 SoftDeCC is working closely with major training centers and academies. This results in a unique experience with training requirements.
Our Learning Management System is designed to adjust to individual corporate learning processes and address evolving challenges. More...

Free Consultancy Appointment
Arrange for your free consultancy appointment to discuss your challenge with us.
Call +49 (0)89 / 309083930.
.webp)




