The Evolution of Continuing Education
Continuing education has changed significantly over the past two decades. While traditional methods of knowledge transfer predominated in the year 2000, today learners demand flexible, personalized, and technology-driven offerings. This shift is not only a result of technological advancements but also of changing needs and expectations of learners.
In this text, we examine the differences in learners' expectations between 2000 and 2024 and highlight the consequences for training providers.
Educational providers that wish to offer training programs funded by the German Federal Employment Agency or job centers must adhere to strict guidelines and certification requirements. These regulations ensure that only high-quality training programs that align with labor market objectives receive funding. For educational providers, this opens up significant opportunities: you can reach a broader audience and benefit from government funding programs.
We provide you with a comprehensive overview of the steps your academy needs to take to become certified to offer government-funded training programs.
Additionally, we show how specialized software solutions can simplify the approval process and significantly improve the training management of these programs.
Learner Expectations in 2000: Traditional Continuing Education
In 2000, continuing education was largely characterized by traditional methods. Learners were generally bound to in-person events that often left little room for interactivity and individual customization.
Learning Motivation:
-
- In 2000, learners were often motivated to participate in training programs to prepare for their current jobs or to receive support from their employers. This motivation was frequently driven by external factors, such as the pressure to adapt to corporate demands or to secure a promotion.
- Participation in training was often a prerequisite for career advancement or even job retention. Many learners viewed continuing education as an obligation rather than an opportunity, which strongly influenced their motivation to learn.
- In 2000, learners were often motivated to participate in training programs to prepare for their current jobs or to receive support from their employers. This motivation was frequently driven by external factors, such as the pressure to adapt to corporate demands or to secure a promotion.
Typical Training Methods:
-
- Training sessions primarily took place in person, often in the form of lectures and seminars. These events were usually unidirectional, meaning the trainer conveyed information while learners passively consumed it.
- Interactive elements and learner engagement were generally not part of the experience. Curricula were often standardized, leaving little opportunity for participants to contribute their interests or learning objectives.
- Training sessions primarily took place in person, often in the form of lectures and seminars. These events were usually unidirectional, meaning the trainer conveyed information while learners passively consumed it.
Technological Landscape:
-
- Digital technologies played a minor role, and content was often static and unengaging. In many cases, handwritten materials or printed scripts were used, lacking multimedia elements.
- E-learning formats were still in development and were only utilized sporadically. The integration of computer technology into the learning process was often rudimentary and mostly limited to printing materials or sending information via email.
- Digital technologies played a minor role, and content was often static and unengaging. In many cases, handwritten materials or printed scripts were used, lacking multimedia elements.
Key Factors for Learners at that Time:
-
-
- Limited personalization of learning content: Training was frequently standardized and offered little room for individual needs. Learners often felt that the materials provided did not align with their specific career goals or interests.
- Content was often dictated by the employer, with little involvement from learners in the decision-making processes. This led to a diminished sense of ownership over the learning material and feelings of alienation.
- Limited personalization of learning content: Training was frequently standardized and offered little room for individual needs. Learners often felt that the materials provided did not align with their specific career goals or interests.
-
Learner Expectations in 2024: Digital and Personalized Continuing Education
Today, learners' expectations have fundamentally changed. In 2024, they demand tailored, flexible, and technology-driven learning opportunities that suit their individual needs.
Learning Motivation Today:
-
- Learners are increasingly motivated to expand their skills to improve career prospects or pursue personal interests. In an era of constant change in the workplace, many recognize that lifelong learning is crucial for professional success.
- Access to information and online resources enables learners to learn more autonomously and responsibly. They actively seek out learning opportunities that help them achieve their goals and advance their careers.
- Learners are increasingly motivated to expand their skills to improve career prospects or pursue personal interests. In an era of constant change in the workplace, many recognize that lifelong learning is crucial for professional success.

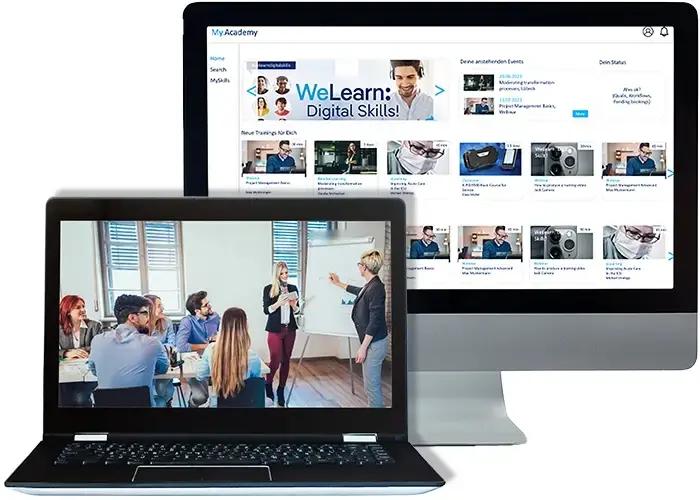
 Learning Platform
Learning Platform
 Testgenerator
Testgenerator
Expectations for Modern Learning Offers:
Flexibility:
- Learners expect to access learning content anytime and anywhere. The ability to access training resources from home or on the go is a crucial criterion for choosing continuing education options.
- Flexibility allows learners to integrate their learning process into their busy schedules, which is vital for many working adults.
Personalization:
- Learning content should be tailored to the individual needs and goals of learners. This can be achieved through adaptive learning technologies that analyze learners' progress and provide relevant recommendations.
- A personalized learning experience enhances content relevance and fosters motivation, as learners feel that the training is directly aligned with their individual career objectives.
Technological Integration:
- Modern learning offers should include interactive elements such as videos, simulations, and gamification to increase learner motivation. Learners seek diverse formats that make learning more interesting.
- The use of social media and online communities is increasingly valued to foster exchange and collaboration in learning. Learners want to share experiences and resources with others and build a network.
Expectations for Training Concepts:
-
- Learners desire immediate applicability of the content in their professional lives. The ability to implement what they have learned right away is a crucial criterion for the success of continuing education.
- Learners desire immediate applicability of the content in their professional lives. The ability to implement what they have learned right away is a crucial criterion for the success of continuing education.
-
- Interactive formats such as online courses, webinars, and workshops are in higher demand than ever. These formats enable active participation and encourage interaction among participants, making learning more effective.

Consequences for Training Providers
The changed expectations of learners have significant implications for the strategies and offerings of training providers. To meet these demands, academies and training centers must rethink and adjust their approaches. Here are the essential points on how modern seminar management software, learning platforms, and LMS can support these efforts:

Adapting Teaching Methods:
-
- Integration of Blended Learning: Modern learning management systems (LMS) allow for seamless integration of in-person and online learning modules. For example, providers can design courses that offer a face-to-face session on the first day, followed by several online sessions where learners can delve deeper into the content. This combination allows for the benefits of both formats to be utilized, enriching the learning experience.
- Creating Interactive Content: Using seminar management software, training providers can create multimedia content (e.g., videos, interactive graphics, simulations) that enhances learner engagement. An example might be a project management course that uses real case studies and simulations to apply what has been learned directly. This makes the content more dynamic and practical.
- Integration of Blended Learning: Modern learning management systems (LMS) allow for seamless integration of in-person and online learning modules. For example, providers can design courses that offer a face-to-face session on the first day, followed by several online sessions where learners can delve deeper into the content. This combination allows for the benefits of both formats to be utilized, enriching the learning experience.
 Easy Administration of Training Offer
Easy Administration of Training Offer
Technological Investments:
-
- Central Management of Content: A robust LMS enables training providers to store and manage all learning materials in one central location. This allows for quick and easy updates to course content, which is especially important to ensure the relevance of information. An example might be a regular update of compliance training that needs to account for legal changes every two years.
- Automated Progress Tracking: LMS offer features for automatically recording attendance and progress data. This allows training providers to see which learners are actively engaged, which modules they have completed, and where they might be struggling. This data is helpful not only for providers but also for learners to monitor their progress and set individual learning goals.
- Central Management of Content: A robust LMS enables training providers to store and manage all learning materials in one central location. This allows for quick and easy updates to course content, which is especially important to ensure the relevance of information. An example might be a regular update of compliance training that needs to account for legal changes every two years.
 Feedback
Feedback
Flexibility and Adaptability:
-
-
-
- Entwicklung von On-Demand-Kursen: Schulungsanbieter können mithilfe von LMS leicht On-Demand-Kurse erstellen, die den Lernenden jederzeit zur Verfügung stehen. Ein Beispiel könnte ein Kurs über die neuesten Software-Tools sein, der so gestaltet ist, dass Lernende bei Bedarf auf spezifische Module zugreifen können, wenn sie diese Informationen benötigen. Diese Flexibilität ist besonders für Berufstätige wichtig, die oft keine Zeit für regelmäßige Schulungen finden.
- Mobile Learning-Funktionen: Viele LMS sind mobil optimiert oder bieten eigene Apps, die es den Lernenden ermöglichen, Inhalte auf Smartphones oder Tablets abzurufen. Ein Beispiel wäre eine App, die es den Nutzern ermöglicht, während ihrer Pendelzeit Lernvideos zu schauen oder Quizfragen zu beantworten, wodurch die Zeit effizient genutzt wird.
- Entwicklung von On-Demand-Kursen: Schulungsanbieter können mithilfe von LMS leicht On-Demand-Kurse erstellen, die den Lernenden jederzeit zur Verfügung stehen. Ein Beispiel könnte ein Kurs über die neuesten Software-Tools sein, der so gestaltet ist, dass Lernende bei Bedarf auf spezifische Module zugreifen können, wenn sie diese Informationen benötigen. Diese Flexibilität ist besonders für Berufstätige wichtig, die oft keine Zeit für regelmäßige Schulungen finden.
-
-

Promoting Engagement and Interactivity:
-
- Gamification Elements: By integrating gamification elements such as leaderboards, badges, and rewards into LMS, training providers can enhance learner engagement. An example might be a points system where learners earn points for completing modules or participating in discussions, which they can exchange for rewards. These playful elements make learning more enjoyable and motivating.
- Virtual Classrooms and Social Learning Formats: Many modern LMS offer features for virtual classrooms, where live sessions, discussion groups, or group projects can take place. Providers can create an interactive learning environment in which learners communicate and collaborate directly with one another, fostering knowledge exchange and a sense of community.
- Gamification Elements: By integrating gamification elements such as leaderboards, badges, and rewards into LMS, training providers can enhance learner engagement. An example might be a points system where learners earn points for completing modules or participating in discussions, which they can exchange for rewards. These playful elements make learning more enjoyable and motivating.
Focus on Learner Success and Personalization:
-
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: Advanced LMS allow training providers to develop adaptive learning paths that adjust to the individual progress of learners. For instance, if a learner is struggling with a specific topic, the system can provide additional resources or alternative explanations. This personalized learning experience not only enhances learner success but also increases participant satisfaction.
- Regular Feedback Mechanisms: LMS provide integrated functions for surveys and feedback tools that enable learners to communicate their opinions and suggestions for improvement directly to providers. This allows providers to quickly respond to learner needs and adjust content accordingly, ensuring continuous improvement of the training offerings.
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: Advanced LMS allow training providers to develop adaptive learning paths that adjust to the individual progress of learners. For instance, if a learner is struggling with a specific topic, the system can provide additional resources or alternative explanations. This personalized learning experience not only enhances learner success but also increases participant satisfaction.
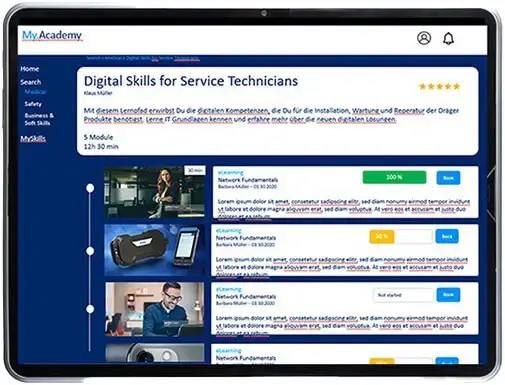 Individual Learning Path
Individual Learning Path
Measuring Success for Training Providers
To determine whether their new, LMS-supported learning offerings are successful, training providers should consider a variety of criteria and metrics:
- Participation and Completion Rates:
- An important indicator of success is the number of learners who enroll in courses and successfully complete them. High completion rates suggest that learners are engaged and find the content valuable. Providers should regularly analyze this data to identify patterns and make adjustments as needed.
- An important indicator of success is the number of learners who enroll in courses and successfully complete them. High completion rates suggest that learners are engaged and find the content valuable. Providers should regularly analyze this data to identify patterns and make adjustments as needed.
- Learner Feedback:
- Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms within the LMS provide valuable insights into how learners perceive the content and the learning experience overall. Questions about learning objectives, content relevance, and platform usability help identify strengths and weaknesses. Positive feedback and high satisfaction ratings are indicators of the success of the offerings.
- Learner Success and Knowledge Transfer:
- Measuring learning outcomes through assessments, quizzes, or practical applications is crucial. Providers should compare learners' performance before and after the course to determine if significant improvements have been achieved. An increase in test scores is a clear sign that learners have successfully absorbed the knowledge.
- Measuring learning outcomes through assessments, quizzes, or practical applications is crucial. Providers should compare learners' performance before and after the course to determine if significant improvements have been achieved. An increase in test scores is a clear sign that learners have successfully absorbed the knowledge.
- User Activity:
- The usage of features within the LMS, such as login frequency, interaction in discussion forums, and utilization of supplementary resources, can provide insight into learner engagement. High activity rates are often a sign that learners are actively engaging with the content.
- The usage of features within the LMS, such as login frequency, interaction in discussion forums, and utilization of supplementary resources, can provide insight into learner engagement. High activity rates are often a sign that learners are actively engaging with the content.
- Long-term Career Development:
- Another key indicator of the success of a learning offering is whether participants experience career advancement or new job opportunities after completing the course. Providers can assess this through follow-up surveys on career development after several months or years to evaluate the long-term benefits of their training.
Conclusion

The changes in learners' expectations since the year 2000 require academies and training providers to rethink their concepts and offerings. While standardized and impersonal training formats often prevailed in the past, today flexibility, personalization, and technology are at the forefront of learning needs. To meet these demands, it is crucial to effectively utilize modern seminar management systems and Learning Management Systems (LMS).
By implementing adaptive learning technologies, interactive content, and continuous feedback mechanisms, training providers can not only enhance learner engagement and satisfaction but also sustainably improve learning outcomes. Collecting and analyzing relevant metrics allows providers to measure their success and continuously optimize their offerings. Ultimately, the ability to adapt to the evolving needs of learners will be essential for the long-term success of academies and training centers in the digital age.

About Us
Since 1998 SoftDeCC is working closely with major training centers and academies. This results in a unique experience with training requirements.
Our Learning Management System TCmanager® is designed to adjust to individual corporate learning processes and address evolving challenges. More...

Free Consultancy
Discuss your Training Challenge with us.
Call +49 (0)89 / 309083930 to arrange for your free consultancy.
.webp)




